Hybrid AF Therapy - Clinical Data
Hybrid AF™ CONVERGE Trial Overview
Procedural Performance
Real World Evidence
References
Indications for Use
Hybrid AF CONVERGE Trial Overview1,2
- Pivotal trial designed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the EPi-Sense® Guided Coagulation System for the treatment of symptomatic persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) as compared to a standalone endocardial catheter ablation
- To demonstrate safety of the Hybrid Convergent procedure for the treatment of symptomatic persistent and long-standing persistent AF
- 153 subjects
88 persistent and 65 long-standing persistent patients - 27 sites
25 in the US, 2 in the UK - Patients between 18 and 80 years of age, with symptomatic persistent AF, refractory or intolerant to at least one class I/III anti-arrhythmic drug and with a left atrium size of ≤ 6.0 cm. There was no limitation on duration of AF.
Hybrid Convergent Procedure Demonstrates an Acceptable Safety Profile1,2
2.9% at 7 DaysNot pre-specified by protocol in line with endocardial studies | 7.8% at 30 DaysPre-specified by CONVERGE protocol |
No Deaths | No Cardiac Perforations | No Atrioesophageal Fistulas
Safety Events reported on all treated patients in Hybrid Convergent arm (n=102):
|
Procedural Performance
99% | Procedural success with Hybrid AF Therapy* *Procedural success defined as lesion pattern and pulmonary vein isolation as demonstrated by entrance and /or exit block. |
20% | Improved efficiency with 41 Minutes saved† in the Hybrid AF endocardial procedure compared to catheter ablation alone †Average time savings |
No significant difference in fluoroscopy time between Hybrid Convergent and endocardial ablation alone
Greater Freedom from AF and AF Burden Reduction in Patients with LSPAF with Hybrid Convergent vs Endocardial Ablation Alone, and Sustained Through 18 Months (7-day Holter)1,2
Greater Freedom from Atrial Arrhythmia with and/or without Anti-arrhythmic Drugs* in LSPAF with Hybrid Convergent vs Endocardial Ablation Alone, and Sustained Through 18 months (7-day Holter)1,2
Real World Evidence with Hybrid AF Therapy
Totality of Evidence Demonstrates 60.5-88% Freedom from Atrial Arrhythmias and Reduced AF Burden Among More Than 1,400 Advanced Afib* Patients Studied
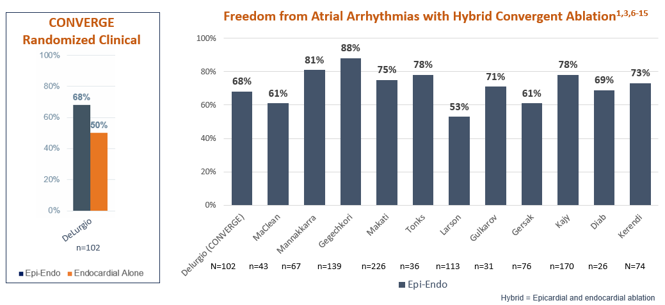
*Defined as persistent or long-standing persistent Afib
Hybrid Convergent Demonstrates Improved AF-Free Survival7
This prospective, single site, observational post-market study evaluated atrial fibrillation (AF)-free survival at 12 months and at 3 years among long-standing persistent AF (LSPAF) patients who underwent the Hybrid Convergent procedure. Outcomes were compared to a matched cohort of 43 patients who underwent catheter ablation alone. Baseline characteristics were similar between groups.
Study duration: 1-3 years
Sample Size: N=43 in Hybrid Convergent arm with matched cohort of N=43 patients in endocatheter ablation arm
Results: The Hybrid Convergent procedure was associated with improved AF-Free survival on and off antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs) versus endocatheter ablation alone at 12 months and at 30.5±13.3 months of follow-up.
Both groups underwent multiple catheter ablations as needed.
Longer-term AF Burden Reduction with Hybrid Convergent Ablation10
This multicenter, retrospective analysis of 226 patients in the TRAC-AF Registry evaluated safety and atrial fibrillation (AF) burden outcomes after Hybrid Convergent procedure with cryo endocardial pulmonary vein isolation.
Study Duration: 12 and 24-month follow-up following a 3-month blanking period from the index procedure
Sample Size: N=226 who underwent Hybrid Convergent procedure with endocardial cryothermy ablation between Nov 2011 and May 2018.
Results: Hybrid Convergent with cryo endocardial ablation resulted in low atrial fibrillation (AF) recurrence rates and marked AF burden reduction at 12 and 24-months post-procedure.
98.5% or greater | 89% or greater |
Secondary analysis demonstrating AF burden reduction in patients continuous monitored by implantable loop recorder, implantable pacemaker or defibrillator
Real World Effectiveness of Same Day Hybrid Convergent Procedure16
This multicenter, retrospective analysis of 182 patients in the TRAC-AF Registry evaluated freedom from atrial arrhythmias after same-day hybrid convergent procedure.
Study Duration: 12- and 18-month outcomes following a 3-month blanking period from the index procedure.
Sample Size: N=182 patients with long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation (> 1 year duration).
Results: Hybrid convergent ablation performed in routine clinical practice continues to be safe and effective in a historically difficult-to-treat patient population.
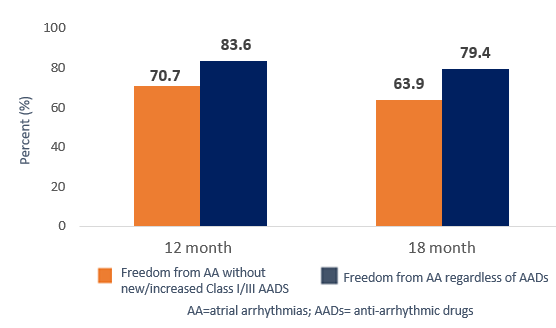
Sustained AF Burden Reduction with Continuous Rhythm Monitoring6
This single center, retrospective analysis evaluated long term AF-free survival among patients with either persistent or long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation (LSPAF) who underwent the Hybrid Convergent procedure.
Study Duration: Mean duration of follow-up was 501 ± 355 days.
Sample Size: N=113 consecutive patients; 88% had either persistent AF or long-standing persistent AF. Most patients (n=92) had continuous rhythm monitoring.
94% of patients had < 5% AF burden at last follow-up
64% of patients were off antiarrhythmic drugs at the last follow-up
53% of patients were free from any AF or atrial tachycardia episode lasting more than 30 sec at 12 months
Longer-term Freedom from Atrial Arrhythmias with Hybrid Convergent Procedure12
This retrospective analysis evaluated 31 patients with persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) who underwent the Hybrid Convergent procedure at a single institution between Oct 2013 and Mar 2017.
Study duration: Median follow up was 17.7 months
Sample Size: N=31 (16 long-standing persistent AF, 15 persistent AF)
Freedom from Atrial Arrhythmia Recurrence with or without Anti-arrhythmic Drugs
Type of Arrhythmia | At 2 Years |
AF Only | 71% |
Atrial Tachyarrhythmias* | 52% |
*After 90-day blanking period; atrial tachyarrhythmias include atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter
At the 2-year follow-up, mean time of recurrence of AF/AFL and AF alone 491 ± 187 days and 417 ± 169 days, respectively.
A total of 16.1% of patients in this cohort had pre-existing hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. These patients are known to have higher recurrence rates and need for antiarrhythmic drugs (AADs) for longer periods of time.
Hybrid AF Therapy Improves Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Heart Failure17
This multicenter, retrospective analysis evaluated left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF, measured with 2-D echocardiography) in patients with pre-existing AF who underwent Hybrid Convergent ablation.
Study Duration: Approximately 1 year
Sample size: 158 patients (155 had persistent or long-standing persistent AF) for which 70 patients had a reduced LVEF of <55% at baseline prior to Hybrid Convergent ablation.
Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction Improved after Hybrid Convergent Ablation
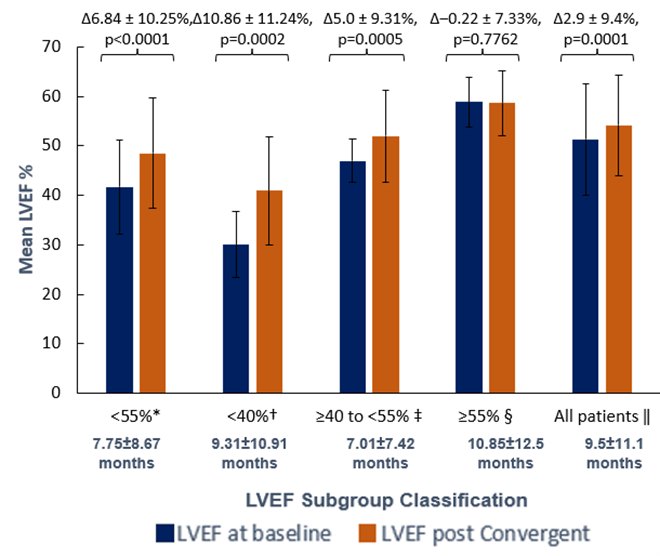
LVEF improvements occurred in patients with reduced LVEF of <55% at baseline. Patients with more severely-to-moderately reduced LVEF (<40%, n=22) experienced the greatest LVEF improvement after hybrid (+10.9%, p=0.0002), thus increasing their EF classification to moderate-to-mild. This study adds to the limited published evidence in support of hybrid to treat patients with AF and depressed LVEF.
Key Points
Hybrid AF Therapy with the | Is the first and only FDA-approved device for minimally invasive ablation therapy to treat long-standing persistent AF—the most prevalent and undertreated AF patient population |
Safety & Effectiveness | Totality of evidence demonstrates reasonable assurance for use of Hybrid Convergent ablation to treat patients with symptomatic drug-refractory long-standing persistent AF |
EP Lab Time Savings | 41 minutes average time saved in Hybrid Convergent endocardial procedure arm of the Hybrid AF CONVERGE Trial |
AF Burden Reduction | Improved reductions in AF burden were demonstrated in the Hybrid AF CONVERGE Trial with similar reductions observed in a real world setting. |
References
- DeLurgio 2020. Circ AE. 13(12):e009288
- Instructions For Use for EPi-Sense® Guided Coagulation System, 2021, IFU-0020.B
- Kerendi F et al. Annals of Thoracic Surgery. 57th Annual STS Meeting, 2021. Abstract
- Tahirkheli M et al. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2023. 81(8): Suppl:74-74
- Pickmans F et al. Circulation. 2022. 146:Suppl 1:14899
- Larson et al. 2020. J of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 31(6): 1270-6.
- Maclean E. et al. 2020. International Journal of Cardiology. 303:49–53.
- Mannakkarra NN et al. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery. 2023; 63(1).
- Gegechkori N et al. 2022. J Afib-EP. 15(4):66-71
- Makati, KJ et al. 2020. Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology. 13, e008556.
- Tonks R et al 2020. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 26(1):13-21.
- Gulkarov I. et al. 2019. J Card Surg. 34:1037-1043.
- Gersak B and J. Jan. 2016. Ann Thorac Surg. 102:1550-7.
- Kajy ML et al. Heart Rhythm. 2024 Apr 6:S1547-5271(24)02329-4
- Diab M et al. Outcomes of convergent procedure in patients with prior AF ablation: Single Center Experience. Heart Rhythm. 20(5): S348.
- Makati et al. 2023. J Am Coll Cardiol. 81(8):Suppl,143
- Oza SR et al. 2024. JAFIB-EP. 17(1):1-5.
Indications for Use
EPi-Sense® Coagulation System/EPi-Sense ST™ Coagulation Device
Australia, Chile, EU Region, Hong Kong, Israel, Kuwait, New Zealand, UK: The EPi-Sense® Guided Coagulation System with VisiTrax® is intended for the coagulation of cardiac tissue using radiofrequency (RF) energy during cardiac surgery for the treatment of arrhythmias including Atrial Fibrillation (AFIB) or Atrial Flutter (AFL).
United States: The EPi-Sense Coagulation System/EPi-Sense ST™ Coagulation Device is intended for the treatment of symptomatic long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation (continuous atrial fibrillation greater than 12 months duration) when augmented in a hybrid procedure with an endocardial catheter listed in the instructions for use, in patients (1) who are refractory or intolerant to at least one Class I and/or III antiarrhythmic drug (AAD); and (2) in whom the expected benefit from rhythm control outweighs the potential known risks associated with a hybrid procedure such as delayed post-procedure inflammatory pericardial effusions. Contraindications include patients with Barrett’s Esophagitis, left atrial thrombus, a systemic infection, active endocarditis, or a localized infection at the surgical site at the time of surgery. Adverse Events: Reported adverse events associated with epicardial ablation procedure may include, but are not limited to, the following: pericardial effusion/cardiac tamponade, pericarditis, excessive bleeding, phrenic nerve injury, stroke/TIA/neurologic complication. Warnings: Physicians should consider post-operative anti-inflammatory medication to decrease the potential for post-operative pericarditis. and/or delayed post-procedure inflammatory pericardial effusions. Physicians should consider post-procedural imaging (i.e. 1-3 weeks post-procedure) for detection of post-procedure inflammatory pericardial effusions. Precautions: Precautionary measures should be taken prior to considering treatment of patients: (1) Deemed to be high risk and who may not tolerate a potential delayed post-procedure inflammatory pericardial effusion. (2) Who may not be compliant with needed follow-ups to identify potential safety risks. To ensure patients undergoing treatment with the EPi-Sense/EPi-Sense ST device are well informed, the benefits, potential risks and procedural outcomes associated with the EPi-Sense/EPi-Sense ST Hybrid Convergent procedure should be discussed with the patient. Physicians should document accordingly in the medical record. Qualified operators are physicians authorized by their institution to perform surgical sub-xyphoid pericardial access. The coagulation devices should be used by physicians trained in the techniques of minimally invasive endoscopic surgical procedures and in the specific approach to be used. Operators should undergo training on the use of EPi-Sense/EPi-Sense ST device before performing the procedure. Safety and effectiveness of concomitant left atrial appendage closure was not evaluated in the CONVERGE study. Follow-up should be conducted at approximately 30 days post procedure to monitor for signs of delayed onset pericarditis or pericardial effusion.
EPi-Sense ST™ Coagulation Device
EU Region: The EPi-Sense ST™ Coagulation Device is indicated for the epicardial treatment of arrhythmias including atrial fibrillation (AF) when augmented with an endocardial ablation, with the aim to restore normal sinus rhythm, reduce AF symptoms, and improve quality of life.

