Atrial fibrillation (Afib) is an abnormal heart rhythm caused by erratic electrical signals in the heart. A normal heart rhythm creates regular electrical signals that are essential for the heart to beat in a steady, rhythmic way to pump blood to all parts of the body. Sometimes these electrical signals become irregular and the heart beats abnormally. Atrial fibrillation is the most commonly diagnosed arrhythmia in the U.S.1
37 Million People Have Atrial Fibrillation Worldwide7

8 million
people are estimated to have atrial fibrillation in the U.S.2
1.2 million
people are diagnosed with atrial fibrillation every year in the U.S.2
1 in 4 adults
over 40 will develop atrial fibrillation in their lifetime.1
Why Atrial Fibrillation Treatment Is So Important
Atrial fibrillation is a progressive disease.3 Unfortunately, atrial fibrillation is often undiagnosed or undertreated. If not properly treated, atrial fibrillation can become worse. There are several stages of atrial fibrillation, depending on how long it lasts.

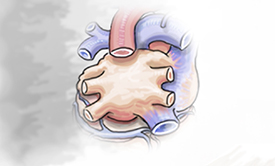
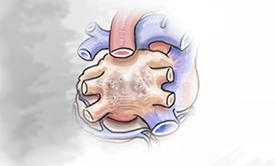
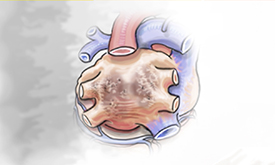
| Paroxysmal means occasional. This stage of atrial fibrillation starts and stops on its own. It can last from 1 to 7 days. This is the first stage of atrial fibrillation. | Persistent atrial fibrillation lasts beyond 7 days and as long as one year. If not treated, atrial fibrillation may advance to the long-standing persistent stage. | Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation symptoms continue beyond one year without stopping. |
| EARLY STAGE | ADVANCED STAGES | |
 |  |  |
| Symptoms for Early Stage Atrial Fibrillation: palpitations, fluttering feeling in the chest, or a rapid, irregular heartbeat. If not effectively treated, atrial fibrillation may progress to more advanced stages. | Symptoms for Advanced Stages of Atrial Fibrillation: Chest pain (angina), chest pressure, lightheadedness, or low blood pressure.4,5 Some people with atrial fibrillation may not be aware of their symptoms and are only diagnosed when they see their physician. | |

| Paroxysmal means occasional. This stage of atrial fibrillation starts and stops on its own. It can last from 1 to 7 days. This is the first stage of atrial fibrillation. |
| EARLY STAGE |
 |
| Symptoms for Early Stage Atrial Fibrillation: palpitations, fluttering feeling in the chest, or a rapid, irregular heartbeat. If not effectively treated, atrial fibrillation may progress to more advanced stages. |

| Persistent atrial fibrillation lasts beyond 7 days and as long as one year. If not treated, atrial fibrillation may advance to the long-standing persistent stage. | Long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation symptoms continue beyond one year without stopping. |
| ADVANCED STAGES | |
 |  |
| Symptoms for Advanced Stages of Atrial Fibrillation: Chest pain (angina), chest pressure, lightheadedness, or low blood pressure. Some people with atrial fibrillation may not be aware of their symptoms and are only diagnosed when they see their physician. | |
Atrial Fibrillation Can Damage Your Heart
Atrial fibrillation causes physical changes to the structure and shape of the heart. It can scar and stretch as well as stiffen your heart muscle. If it is not properly treated, it can lead to other health problems. If you have—or continue to have—atrial fibrillation, you are at 5 times higher risk for stroke.6 It is important to talk to your health care provider if you believe you have atrial fibrillation, or if you have atrial fibrillation and your current treatment is not working.
Scarring
Atrial fibrillation can lead to scarring of the atrial tissue. The scarring is also called fibrosis. (The atria are the heart’s upper chambers.)
Stretching
Eventually the heart tissue becomes stretched, too. As the walls of the heart are stretched, the heart muscle becomes weaker.
Stiffening
The heart muscle gets stiffer, so that it’s harder for the heart to pump correctly.
These changes can cause more episodes of atrial fibrillation. Read about the other health problems caused by atrial fibrillation.
How Do I Find the Right Treatment for My Atrial Fibrillation?
Be sure to talk to your health care team about how to find the right treatment for your atrial fibrillation. Click here to learn more.
Click here to Find a Specialist.
Symptoms, Risk Factors and Triggers for Atrial Fibrillation
What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation – risk factors and triggers for atrial fibrillation
Importance of Treatment
If not properly treated, atrial fibrillation gets more severe. Atrial fibrillation can lead to stroke, heart failure, and other health problems. Read about how atrial fibrillation impacts your heart and other health risks.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
Learn about diagnosis and treatment options
Frequently Asked Questions
Find answers to questions about atrial fibrillation
- Lloyd-Jones, D.M., Wang, T.J., Leip, E.P., Larson, M.G., Levy, D., Vasan, R.S., D'Agostino, R.B., Massaro, J.M., Beiser, A., Wolf, P.A., Benjamin, E.J. (2004). Lifetime risk for development of atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 110, 1042-1046. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000140263.20897.42
- Colilla, S., Crow, A., Petkun, W., Singer, D.E., Simon, T., Liu, X. (2013) Estimates of current and future incidence and prevalence of atrial fibrillation in the U.S. adult population. American journal of cardiology, 112(8), 1142-1147. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2013.05.063
- Shukla, A., & Curtis, A. B. (2014). Avoiding permanent atrial fibrillation: treatment approaches to prevent disease progression. Vascular health and risk management, 10, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.2147/VHRM.S49334
- Calkins, H., Hindricks, G., Cappato, R., Kim, Y. H., Saad, E. B., Aguinaga, L., Akar, J. G., Badhwar, V., Brugada, J., Camm, J., Chen, P. S., Chen, S. A., Chung, M. K., Nielsen, J. C., Curtis, A. B., Davies, D. W., Day, J. D., d'Avila, A., de Groot, N., Di Biase, L., … Yamane, T. (2017). 2017 HRS/EHRA/ECAS/APHRS/SOLAECE expert consensus statement on catheter and surgical ablation of atrial fibrillation. Heart rhythm, 14(10), e275–e444. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2017.05.012
- Barbarossa, A., Guerra, F., & Capucci, A. (2014). Silent atrial fibrillation: a critical review. Journal of atrial fibrillation, 7(3), 1138. https://doi.org/10.4022/jafib.1138
- Benjamin E.J., Muntner, P., Alonso, A., Bittencourt, M.S., Callaway, C.W., Carson, A.P., Chamberlain, A.M., Chang, A.R., Cheng, S., Das, S.R., Delling, F.N., Djousse, L., Elkind, M.S.V., Ferguson, J.F., Fornage, M., Jordan, L.C., Khan, S.S. ... Virani, S.S., and On behalf of the American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. (2019). Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics—2019 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association.
Circulation, 139, e56–e528. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000659 - European Heart Journal – Quality of Care and Clinical Outcomes (2021) 7, 574-582 doi: 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcaa061

